Physics 2: RLC Circuits
Given an RL charging circuit with battery voltage, = 30 V, an inductor with L = 30 mH, and a resistor of 50 , how long will it take for the current to reach 75% of its maximum value?
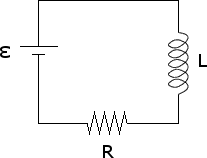
In the circuit below, the switch sw has been open for a long time. At t = 0, the switch closes. Write, as a function of time for t > 0:
B. the energy in the inductor
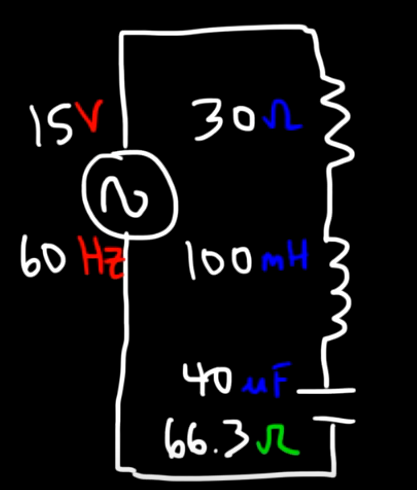
A 40 uF capacitor is in series with a 100 mH inductor, a 30 ohm resistor, and a 15V AC signal with a frequency of 60Hz. (a) Calculate the capacitive reactance and the inductive reactance in the circuit. (b) Determine the impedance. (c) Calculate the rms current in the circuit. (d) Calculate the voltage across the resistor, the inductor, and the capacitor. (e) How much power is consumed in the circuit? (f) What is the resonant frequency of the circuit?
A 50 F capacitor is charged to 12V and then connected across a 60 mH inductor. What is the maximum current that will flow in the circuit?
A LC circuit consists of a 10 mH inductor and a 1 microfarad capacitor. If the maximum instantaneous current is 0.1 A, what is the greatest potential difference across the capacitor?
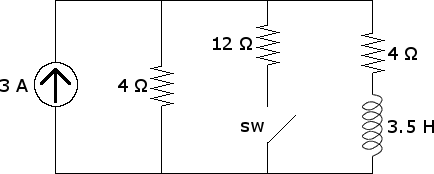
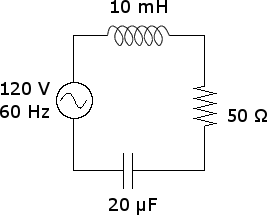
Calculate the impedance in the circuit shown below as well as the current flowing in each element.
Before the switch is closed, the capacitor is uncharged and all currents are zero.
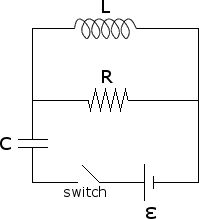
B. A long time after the switch is closed, find the voltage drop across and the current through the capacitor, inductor, and resistor.
What are the maximum voltage drops across each element? What is the average power dissipated in the circuit?
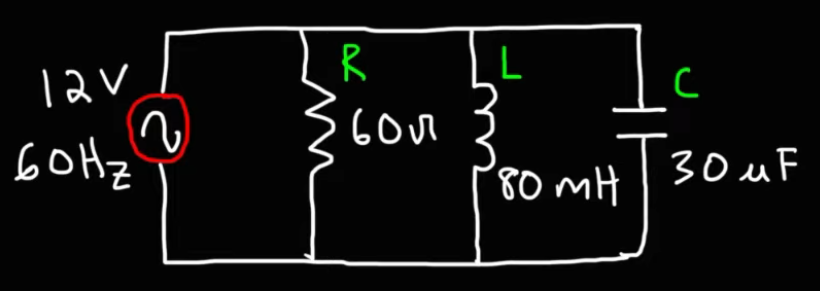
An AC circuit with a 450 Ωresistor, 1.7 H inductor, and a 10 μF capacitor oscillates at a frequency of 50 Hz. If the source voltage is 220 V (rms), find the following:
inductive reactance
capacitive reactance
impedance
rms current of circuit
max voltage across resistor
rms voltage across capacitor
max voltage across inductor
average power dissipated in circuit
power factor
phase angle between current and voltage
resonant frequency of the circuit